
The discount on notes payable account is a balance sheet contra liability account, as it is netted off against the notes payable account to show the net liability. The $25,000 balance in Equipment is accurate, so no entry is needed in this account. As an asset account, the debit balance of $25,000 will carry over to the next accounting year. The $1,500 balance in the asset account Prepaid Insurance is the preliminary balance. The correct amount is the amount that has been paid by the company for insurance coverage that will expire after the balance sheet date.
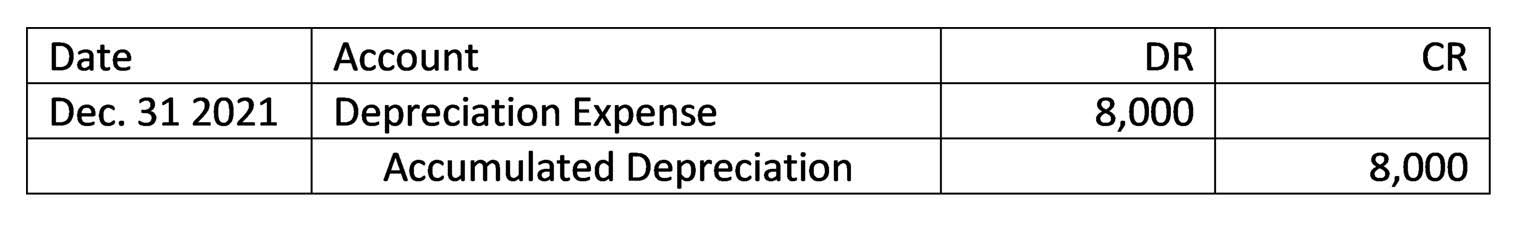
Journal Entry for Prepaid Expenses
When a customer fails to repay the amount owed it is known as a bad debt. According to the calculations, the total amount due on May 1st will be the principal amount plus interest payable. The principal of $10,475 due at the end of year 4—within one year—is current. The principal of $10,999 due at notes payable journal entry the end of year 5 is classified as long term. In the following example, a company issues a 60-day, 12% interest-bearing note for $1,000 to a bank on January 1.

Issuance of notes payable to extend the period of the loan.
- That part of the accounting system which contains the balance sheet and income statement accounts used for recording transactions.
- These scenarios demonstrate how companies handle the early extinguishment of debt, whether for notes payable or bonds payable.
- When a zero-interest-bearing note is issued, the lender lends to the borrower an amount less than the face value of the note.
- The accounting term that means an entry will be made on the left side of an account.
- This journal entry of issuing the note payable will increase both total assets and total liabilities on the balance sheet.
When the allowance account is used, the company is anticipating that some accounts will be uncollectible in advance of knowing the specific account. When a specific account is identified as uncollectible, the https://www.bookstime.com/articles/what-are-notes-receivable Allowance for Doubtful Accounts should be debited and Accounts Receivable should be credited. The credit balance in this account comes from the entry wherein Bad Debts Expense is debited.
- A business may borrow money from a bank, vendor, or individual to finance operations on a temporary or long-term basis or to purchase assets.
- Additionally, they are classified as current liabilities when the amounts are due within a year.
- However, the notes payable are typically transacted with a single lender; for instance, a bank or financial institution.
- What distinguishes a note payable from other liabilities is that it is issued as a promissory note.
- Example Step 1 – Electricity Expense of 1,000 is unpaid on the balance sheet date.
- After an event is identified to have an economic impact on the accounting equation, the business event must be analyzed to see how the transaction changed the accounting equation.
- When a note’s maturity is more than one year in the future, it is classified with long-term liabilities.
What Is Notes Payable, and How Do You Record Them in Your Books?
- If the bonds are issued at a discount (below face value), the entry includes a discount on bonds payable account.
- If the bonds are issued at a premium (above face value), the entry includes a premium on bonds payable account.
- Under the accrual method of accounting, the company will also have another liability account entitled Interest Payable.
- There was an older practice of adding interest expense to the face value of the note—however, the convention of fair disclosure under truth-in-lending law.
- This ensures that the financial statements accurately depict the company’s obligations and expenses.
The balance sheet shows the current portion of notes payables, which is the amount due within one year, and the long-term what are retained earnings portion, which is the amount due after one year. The interest payable account is also presented on the balance sheet as a current liability. The income statement shows the interest expense account, which represents the interest accrued on notes payables during the period. The presentation of notes payables on financial statements provides stakeholders with information about a company’s debt and interest expense.


If you want to minimize the number of adjusting journal entries, you could arrange for each period’s expenses to be paid in the period in which they occur. For example, you could ask your bank to charge your company’s checking account at the end of each month with the current month’s interest on your company’s loan from the bank. Under this arrangement December’s interest expense will be paid in December, January’s interest expense will be paid in January, etc. You simply record the interest payment and avoid the need for an adjusting entry. Similarly, your insurance company might automatically charge your company’s checking account each month for the insurance expense that applies to just that one month.
Another acceptable alternative is to list them by maturity value, from the largest to the smallest. This method spreads the total interest expense evenly over the life of the bond. If the interest is not paid immediately, the credit would be to Interest Payable instead of Cash. This entry shows the extra amount received over the face value, which will be amortized over the bond’s life.
